ASTM A335 P5, P9, P11, P22, P91 Pipe

ASTM A335 pipe, also known as Chrome-Moly Alloy Pipe, is widely used in various industries for high temperature and high pressure services. It is available in different grades such as P5, P9, P11, P22, and P91. Market data shows that it is one of the most commonly used alloy pipes in industries such as boiler manufacturing, heat exchangers, power stations, and high and super high pressure vessels.
Why is there such a high demand for ASTM A335 pipe in these specific industries? How familiar are you with this type of pipe? What are the most prominent grades within this standard?
The following article will tell you all the things you need to know about this pipe.
Listed topics
What is ASTM A335 pipe
Standard specification
Featured Grades
Referred standards to manufacture this pipe
Raw steel material that used for the production
Tests involved
Things you need to notice when placing an order
What is ASTM A335 pipe?
ASTM A335 pipe, also known as ASME S/A335 Chrome-Moly pipe, is a type of seamless pipe that is specifically designed for high-temperature environments. It can withstand temperatures ranging from 540 to 750 °C.
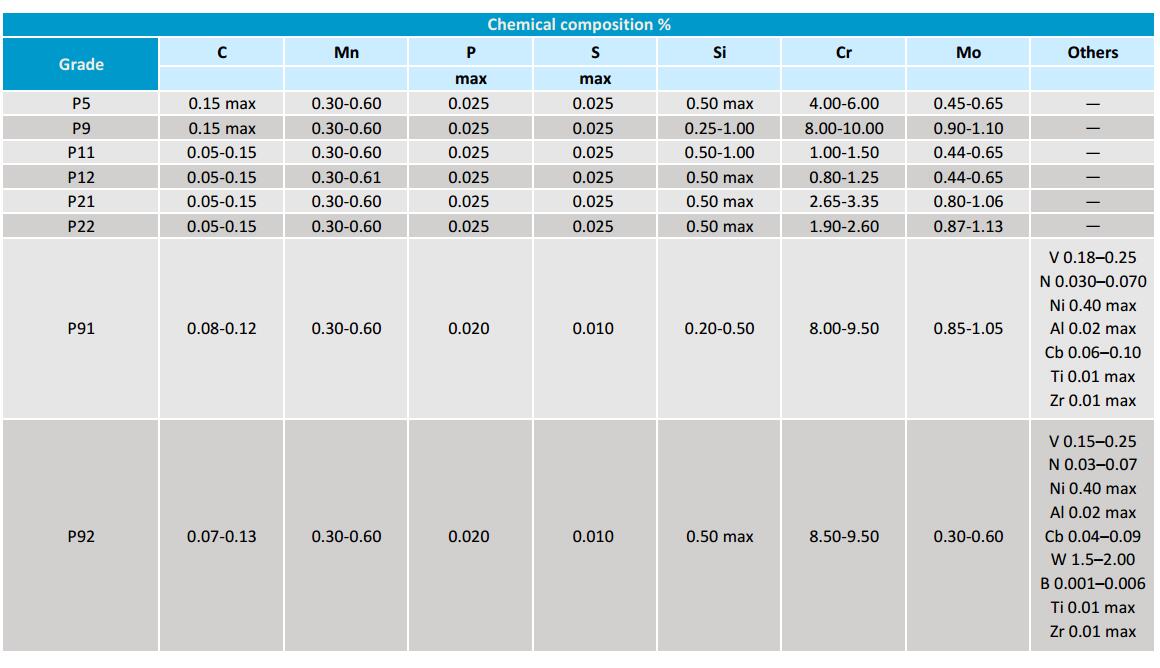
A335 pipes are commonly referred to as chrome moly pipes due to their high content of Chromium and Molybdenum. The presence of Molybdenum enhances the strength, resistance, elasticity, hardenability, and overall quality of the pipe. It also improves the high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance of the steel. Molybdenum plays a crucial role in preventing softening, limiting grain growth, and reducing the risk of embrittlement.
Key Elements Chromium for this pipe
Chromium is an essential element in the production of stainless steel. When the chromium content exceeds 12%, the material can be classified as stainless steel. Chromium provides excellent resistance to oxidation, even at elevated temperatures. It also improves the hardness, tensile strength, and yield strength of the material at standard temperatures. The composition of chrome-moly pipes makes them ideal for use in power plants, refineries, petrochemical plants, and other oil field services where transportation under high temperatures and pressures is involved.
ASTM A335 Standard Specification and Scope
According to ASTM International, ASTM A335 is the standard specification for seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High Temperature Service. This specification covers pipes with alloy material, manufactured in seamless form, and with nominal wall and minimum wall thickness. The pipes specified under this standard are suitable for bending, flanging, and other similar processing and formations. Additionally, they are also suitable for fusion welding.
Therefore, ASTM A335 pipe material can also be used in the manufacturing of pipe fittings such as elbows, tees, reducers, and so on.
A335 P5, P9, P11, P22, P91 Pipe Chemical Composition
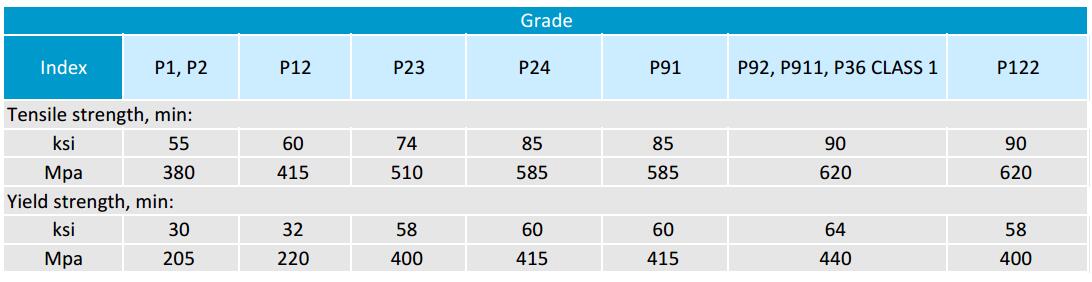
ASTM A335 Pipe Mechanical Properties
Referred standards ASTM
a. ASTM A999/ A999M, Standard specification for common requirements for stainless and alloy steel pipe
b. ASTM A92, Hardness test methods for steel materials
c. E213, Instructions and practice for ultra sonic testing of steel pipe and tube
d. E309 Eddy-Current Examination methods for steel pipe products
e, E381, Inspection methods for steel bars, beams, profiles, billets and forgings.
f, E527, Numbering metals and alloys practices
g, E570, Instructions for flux leakage examination of ferromagnetic steel pipe products
Nominal Pipe Size
ASME B36.10M dimensions standard for welded and seamless steel pipe
Raw steel material that used for the production
The pipe material can be either hot finished or cold drawn, and the related heat treatment is required for different grades. For Grade P2 and P12, the steel should be manufactured using coarse-grain melting procedures.
Featured Grades P5, P9, P11, P22, P91 pipes
These chrome moly pipes are available in different grades, namely ASTM A335 P9, P11, P22, and P91. In some cases, they may also be referred to as P Grade pipes.
P11, P22, and P91 pipes are commonly used in the power industry and petrochemical plants, while P5 and P9 pipes are typically used in refineries.
ASTM A335 P91 pipes – High Pressure Boiler Pipes
It is important to note that ASTM A335 Grade P91 pipe is a high-grade pipe that is commonly used for high-pressure boilers. P91 pipe is particularly suitable for bending, flanging, and similar operations, including welding. The steel material must adhere to specific chemical composition, tensile properties, and hardness requirements.
There are two variants available: ASTM A335 P91 alloy steel pipe and high-pressure boiler pipes. The range of these pipes is dependent on their size, which is determined by their specific usage. The length of the pipe will be subject to a hydrostatic test, and there will also be a non-destructive examination performed in accordance with the specifications.
As a result, chrome moly pipe is widely used in the power generation and petrochemical industries due to its corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. This makes it a cost-effective choice for these industries.
Tests involved
Some of the common tests conducted include transverse and longitudinal tension tests, flattening tests, hardness tests, and bend tests. In the case of a material heat test conducted in a blast furnace, it will be performed on 5% of the pipes manufactured from each lot.
If the diameter of the pipe exceeds NPS 25, the diameter to wall thickness ratio should typically be 7.0 or less. For NPS 10 and thicker pipes, the flattening test is only conducted with the approval of the purchaser.
Things you need to notice when placing an order
When sending an inquiry or placing an order for ASTM A335 pipe, the following specifications should be verified:
a. Length per piece and the quantity (Specified in feet, meters or pieces)
b. Material Name (Seamless alloy steel pipe)
c. Grade (P5, P9, P11, P22, P91 pipe etc)
d. Manufacturing types (hot finished seamless or cold drawn seamless)
e. Size to described as below ways:
1. NPS and Schedule Number (According to ASME B36.10, for example NPS 7 inch and Sch 40)
2. OD or ID and nominal or minimum wall thickness (inch or mm)