316L/316H/316Ti Stainless Steel Pipe
Standard: ASTM A312, ASME SA312, ASTM A269, ASTM A270
Common Use Grades: 316, 316L, 316H, 316Ti, 316N, 316LN
Diameters: From 1/8 inch to 30 inch.
Wall thickness: SCH 10S, 40S, 80S
Length: 20ft, 40ft, Single Random Length, Double Random Length and Customized
316 stainless steel pipe is a type of stainless steel pipe made from 316-grade stainless steel, which is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. It includes molybdenum, which enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments, making it ideal for marine applications and environments where exposure to saltwater or harsh chemicals is a concern.
316/316L/316H stainless steel pipe normally refers to ASTM A312 TP316 pipe. It covers TP316, TP316L, TP316H, TP316Ti, TP316N, TP316LN, major difference between these grade is the chemical composition on carbon, Ti, Nitrogen.
316 stainless steel pipes, fittings, flanges, plates reference standard:
Stainless steel pipes:ASTM A312 TP316/TP316L/TP316H, ASTM A269, ASTM A270
Stainless steel pipe fittings: ASTM A420 WP316/WP316L/WP316H/
Stainless steel flanges: ASTM A182 F316/F316L/F316H
Stainless steel plates: ASTM A240 Type 316/316L/316H
German standard: DIN17400 1.4404
European standard: EN10088 X2CrNiMo17-12-2
316/316L vs 304/304L
Type 316/ 316L/316H are austenitic stainless steel intended for use in applications that require high strength, toughness and workability, as well as enhanced corrosion resistance. Compare to 304 stainless steel, 316 contains a higher percentage of molybdenum (Mo 2%-3%) and nickel (Ni 10% to 14%), Molybdenum has better overall corrosion resistance, especially for pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments. 316 has excellent toughness and mechanical properties at sub-zero temperatures, suitable for cold rolling, continuous mill plate and plate millplate form, thickness range up to 60 inch.
ASTM A312 TP316/316L/316H/316Ti/316LN Chemical Composition
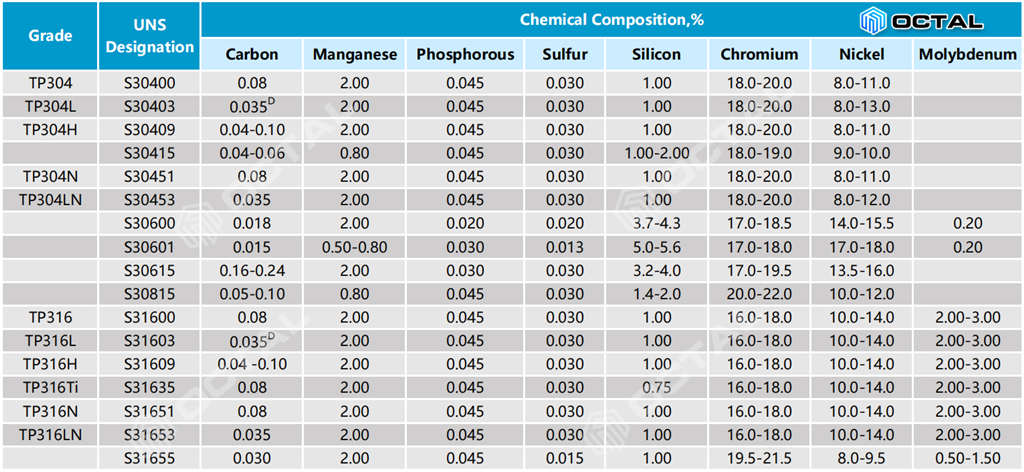
316 Stainles Steel Pipe Mechnical Strength
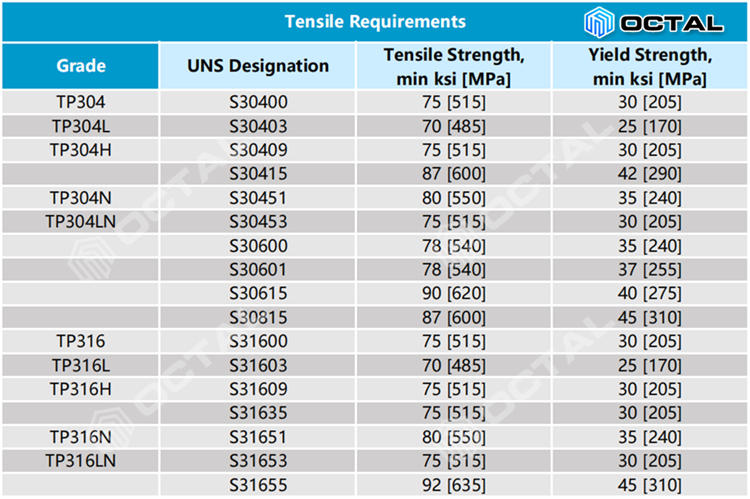
ASTM A312 TP316 316L 316H 316LN Mechnical Strength
316L/TP316L Stainless Steel Pipe
Grade 316L refers S31603 UNS desination 1.4404, it has better corrosion resistance than TP316 because of the lower Carbon content. 316L maximum carbon content 0.03% which 316 maximum 0.08%, higher carbon will increase intergranular corrosion. Therefore, 316L is suitable for applications where carbon precipitation needs to be avoided. This stainless steel is widely used for welding the components, its special carbon content combined with welding ensures maximum resistance to general corrosion, especially applicable for heavy duty components.
316L is considered more resistant to oxidation than Type 316, especially in warm marine environments. Again, its low carbon content protects it from carbon precipitation. The metal also exhibits resistance at extremely low temperatures, even down to cryogenic levels. In terms of heat resistance, 316L exhibits better creep resistance, fracture stress resistance and overall strength than other stainless steel grades.
Many of the same working practices that are valid for Type 316 can also be used for 316L, including weldability and cold work hardening. In addition, 316 does not require post-service annealing to maximize its corrosion resistance, but annealing may be used in some cases.
316H/TP316H Stainless Steel
Grade 316H refers S31609, carbon content 0.04% to 0.10%, it provides higher temperature resistance than 316L.
316Ti/TP316Ti
Stainless steel 316Ti is known as a stable grade of the 316 type and is also one of two 316 stainless steels recommended for higher temperature applications. This grade contains a small amount (usually only 0.5%) of titanium. While it still shares many of the properties of other 316 grades, the addition of titanium protects 316Ti from precipitation at high temperatures, even with prolonged exposure.
Molybdenum is also added to the composition of 316Ti. Like other 316 grades, molybdenum provides enhanced protection against corrosion, chloride solution pitting and strength when placed in high temperature environments. However, its high temperature resistance is also compounded by its titanium content, which makes 316Ti immune to precipitation at these temperatures. In addition, the metal is resistant to acids such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acid sulfates.
316Ti is commonly used in heat exchangers, paper mill equipment and building components in marine environments.
TP316LN/316N
316N: Nitrogen (N) is added to 316 stainless steel to increase the strength without reducing the plasticity, so that the thickness of the material is reduced. For higher strength parts with better corrosion resistance.
316LN is likewisely 316L with N added, has better corrosion resistance than 316N.
TP316/316L/316H/316Ti Stainless Steel Pipe Applications
TP316/316L seamless pipe is used for liquid or gas pressure transfer in water treatment, waste water treatment, petrochemical, chemical, pharmaceutical and other industries. And structural applications include handrails, poles and support pipe for salt water and corrosive environments. Compared with TP304 stainless steel, TP316 stainless steel pipe has lower weldability, therefore it is not used as often as welded pipe unless its superior corrosion resistance exceeds weldability.
316 Stainless Steel Pipe Key Properties and Applications
Corrosion Resistance: It is highly resistant to corrosion, especially against chlorides and acidic environments. This makes it suitable for chemical processing applications.
High-Temperature Strength: 316 stainless steel maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, making it useful in high-temperature applications.
Durability: The material is tough and durable, providing longevity and reliability in various applications.
Applications:
Marine environments (boats, ships)
Chemical and petrochemical processing
Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Food and beverage industry
Architecture and construction
Forms Available: 316 stainless steel pipe can be found in various forms, including seamless and welded pipes, and comes in different sizes and schedules to meet specific requirements.
Overall, 316 stainless steel pipe is a versatile material used in many industries due to its balance of strength and corrosion resistance.



















