Steel Pipe Fittings & Accessories
Range of Sizes: 1/2” to 48”
Range of Thickness: SCH 5, SCH 10, Schedule 40, Schedule 80, SCH XS, SCH XXS etc.
Fittings Types: Welded pipe fittings, socket weld pipe fittings, flanged fittings, threaded fittings.
Materials: Carbon steel, Alloy steel, Galvanized and Stainless steel pipe fittings
Standards and Grades: ASTM A234 WPB, WP1, WP5, WP9, WP11, WP22; ASTM A403 304/L, 316/L; ASME B 16.9/11; MSS SP-75;
Steel pipe fittings are components used to connect, control, or change the direction of steel pipes in various applications, including plumbing, oil and gas, and industrial systems. They come in various shapes and sizes, designed to fit specific pipe dimensions and configurations. Common types of steel pipe fittings include:
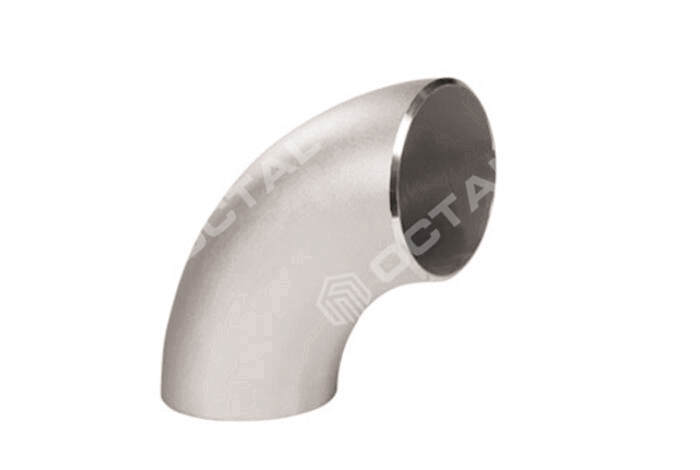
- Elbows: Used to change the direction of the piping, typically at angles of 90 or 45 degrees.
- Tees: Allow for branching off the main pipeline, creating a T-shaped connection.
- Reducers: Used to connect pipes of different diameters, allowing for a smooth transition between sizes.
- Caps: Used to seal the end of a pipe, preventing flow.
- Flanges: Used to connect pipes, valves, and other equipment, providing a strong and secure joint.
Steel Pipe Fittings Types and Applications
To get a better known to pipe fittings, here we classify them into different types from different sides.
• According different body material for indsustrial pipelines, there are
Stainless steel pipe fittings
Carbon steel pipe fittings (Black steel pipe fittings)
Alloy steel pipe fittings
• According different coatings, there are
Black painted
PE coated
Cladding stainless steel or alloy steel
Galvanized steel pipe fittings (zinc coated)
• According different industrial purposes, there are
Oil and gas pipelines
Chemical plants
Food industry
Power stations
Fire sprinkler pipe fittings
• According to different connection type, there
Butt weld fittings type
Socket weld fittings type
Threaded type
Flanged type
On the other hand, when we talked about steel elbow, tees, cross or reducer, what are they?
They are the product name that installed exactly at the places in pipelines for playing the different functions and roles.
How to describe a steel pipe fitting correctly
Therefore, when you place an order or make an inquiry, the sample description will be like “90 degree stainless steel elbow long radius”, “carbon steel equal tee / reducing tee”, added with specific standards, diameters and wall thickness class, then we will know what exactly you are looking for.
Below let’s see how to range steel fittings from applications.
Application Types
Steel Elbow and Bends: For to change the direction of the pipeline
Steel Pipe Tee: To connect pipes from 3 directions.
Cross: To connect pipes from 4 directions.
Reducer (Con. Reducer – Ecc. Reducer): Reduce the flow rate of the line pipe system;
Steel Cap: End the pipelines, to seal the pipe.
Nipple
Coupling
Sockolet
Weldolet
Threadolet
Pipe Union
Gasket (Ring)
Line Blanks
Steel Elbow
In the pipe system, steel pipe elbow changes the pipe direction.
45, 90 and 180 degree elbow are the most commonly used. Elbow materials have cast iron, stainless steel, alloy steel, malleable cast iron, carbon steel, nonferrous metals and plastics. The connection ways between elbow and pipe that include flange connection, hot melt connection, fused connection, threaded connection and socket connection.
According to the production process, elbow can be divided into: welding elbow, stamping elbow, pushing elbow, casting and butt welding elbow.
Based on its radius of curvature, elbow can be divided into long radius elbow and short radius elbow
Long Radius Elbow (R=1.5D): Commonly adopted;
Short Radius Elbow (R=1.0D): Usually used in low pressure fluid and size-limited situation. R—elbow diameter, D—radius of curvature.
Steel Pipe Tee
Steel Pipe tee is used for the place where three pipes are assembled. It mainly used to change the direction of fluid in the branch pipe.
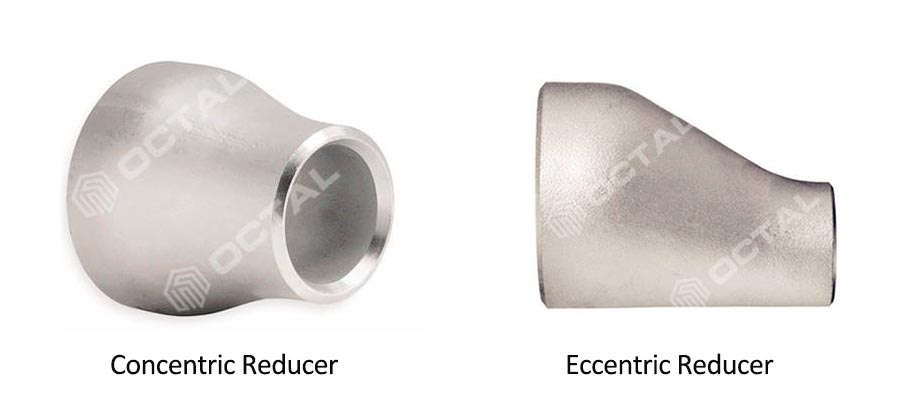
Steel Reducer
There are two types concentric reducer and eccentric reducer.
Reducer is one of the chemical pipe fittings that can connect two different diameter pipe. It also divided into concentric and eccentric reducer. Reducer material includes stainless steel reducer, alloy steel reducer, different diameter carbon steel reducer and so on.
Connection types
According to different connection types, steel pipe fitting can be divided into four categories:
Welded pipe fittings
Socket weld pipe fittings
Threaded pipe fittings
Flanged pipe fittings.
Welded steel pipe fitting
Welded steel pipe fittings ranges in butt weld and socket weld.
A welded pipe fitting connected to pipe by welding, it is mainly used for connecting with steel pipe. It is especially suitable for long pipelines, but not convenient for disassembling pipes frequently. It can be soldered or brazed, the latter often used for copper piping. Welded steel pipe fittings include elbow, flange, tee, reducer, head and other types.
Butt weld fittings
Usually with plain ends or beveled ends, and welding directly with pipe ends.
Socket weld pipe fittings
Socket welding is to install the pipe end into the valve body and perform welding. It has shape similar to internal thread connection after forming. Socket welding fittings is generally used for small diameter less than or equal to DN40, which is more economical. Butt welding is generally used for DN40 or more. The connection form of socket welding is mainly used for small diameter valves and pipes, pipe fittings and pipe welding. Because the wall thickness of small diameter pipe is generally thin, easy to edge and ablation, so it gets more difficult for butt welding, so people will go for socket welding.
Threaded pipe fittings
Threaded pipe fittings are commonly used in water and gas pipes. With small diameter, including compressed air pipe and low pressure steam pipe. The common materials of threaded pipe fittings have forged steel, cast steel, cast iron and malleable iron. Threaded pipe fittings mainly include internal pipe, external pipe, live pipe connection, reducer and so on.
Flanged pipe fittings
The flange pipe fitting belong to the welded pipe fitting. Its material have various kinds, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel and so on.
Steel Pipe Fittings material standard and grades
As we talked above, based on materials for making the fittings, the are carbon, stainless, or alloy steel, so what are the related standards for these materials?
Material Standard
ASTM A234, for carbon and alloy steel
ASTM A105, for carbon flanges
ASTM A403, for stainless steel pipe fittings
ASME/ANSI B16.9 Factory-Made Wrought Steel Butt-welding Fittings
ASME/ANSI B16.11 Forged Steel Fittings, Socket-Welding and Threaded
MSS SP-75
EN10253-1, DIN2605-1, JIS B2311
GB/T12459, GB/T13401
SH3409, SH3409
HG/T12459, HG/T21631
DL/T695, GD2000
SY/T0518, SY/T0609, SY/T0510
Body material:
For Carbon Steel Pipe Fittings: A234 WPB, A420 WPL6, MSS-SP-75 WPHY 42, 46, 52, 56, 60, 65 and 70.
For Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings: ASTM A403 WP 304, 304L, A403, 316, 316L, 317, 317L, 321, 310 and 904L, etc.
For Alloy Pipe Fittings: A234 WP1, WP5, WP9, WP11, WP22, WP91 etc.
More material for Steel Pipe Fittings are: 16Mn, 16MnR, 12CrMo, 15CrMo, 12Cr1MoV, 0Cr18Ni9, 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 0Cr18Ni12MoTi, 00Cr19Ni10, 00Cr17Ni12Mo2, etc
Stainless steel pipe fittings
Stainless steel pipe fittings is usually used for corrosive environments, to protect against pipelines from acid corrosion, for industrial purposes the mainly standard is ASTM A403, this specification includes wrought stainless steel fittings for pressure pipelines. There are several grades under this standard but most used are A403 WP 304, 304L, or 316 and 316L.
Galvanized steel pipe fittings
First of all, galvanized steel pipe fitting includes malleable cast iron pipe fittings (lower pressure for plumbing) and carbon steel pipe fittings (for higher pressure), these two types has a big differences and for different usage.
On the other hand, there are cold galvanized and hot dipped galvanized, butt weld pipe fittings usually apply hot galvanized.
Common standard for carbon and alloy steel pipe fittings: ASTM A234
Chemical composition:
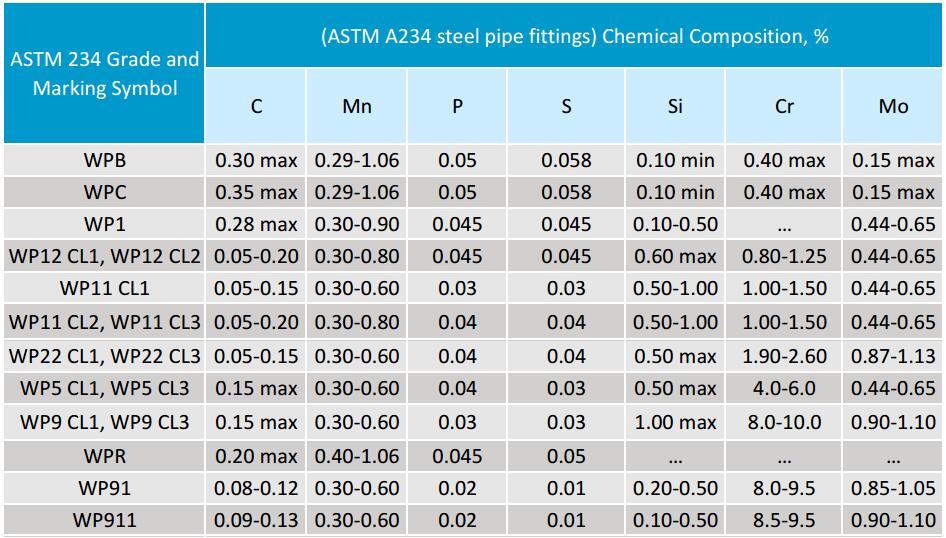
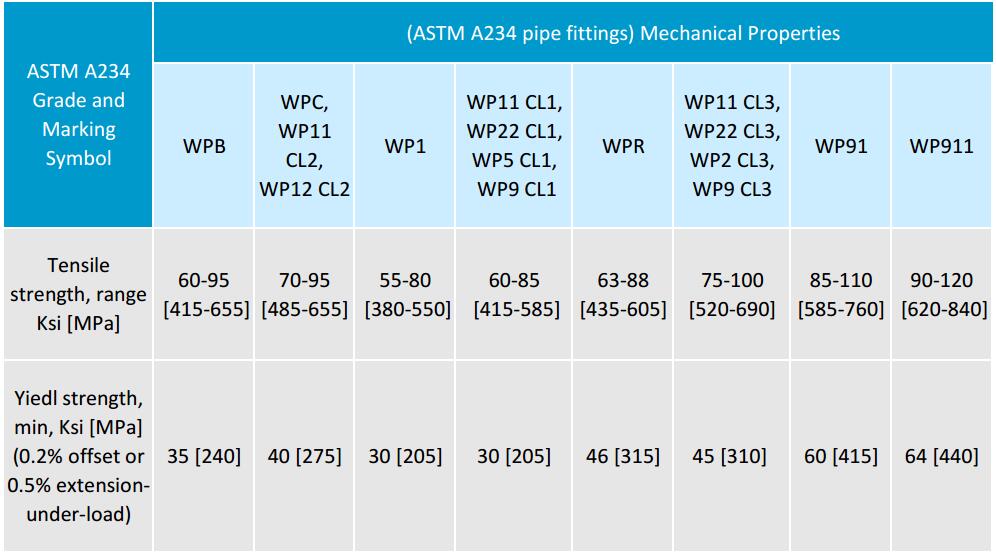
Mechanical properties
Range of Sizes for Steel Pipe Fittings and Accessories
For butt weld fittings sizes available in: 1/2”, 1”, 2”, 3”, 4”, 6”, 8”, 10”, 12”, 16”, 20” to 48”.
For socket weld and threaded pipe fittings sizes in: 1/2”, 1”, 1/2”, 2” and up to 4”.
Thickness for butt weld fittings: SCH 5, SCH 10, SCH 40, SCH STD, SCH 80, SCH XS, SCH 160 and SCH XXS etc.(Schedule 40 steel pipe fittings, and schedule 80 pipe fittings are mostly used.)
Pressure class for socket weld fittings: 3000#, 6000#, 9000#; For threaded pipe fittings pressure ranges in 2000#, 3000# and 6000#
(Flange and gaskets thickness usually described as from 150#, 300#, 600# and up to 2500#. This is different with butt weld fittings but similar to socket weld fittings.)
Our Supply scope regarding steel pipe fittings
Octal supplies steel pipe acceossories and pipe fittings applicable to different industrial areas, Oil & Gas transportaion, Chemical Plant, Power Station, Water Treatment, Refining etc

































Recent Comments